Which one is more sweet, a mango, or an apple? You could only answer this question if you have tasted both fruits. Same as its differentiation. You can easily differentiate two things when you have complete information about them. For that, you must be known to their features individually in detail.
I am here writing this article. I am going to differentiate two things based on relevant information.
I want you all to know about both things. That is why I have given a straightforward example above, which will help you to understand a little bit.
First, the core concept of RAM should clear. RAM stands for Random Access Memory. RAM is a kind of computer memory. It usually stores data and machine codes. It can be changed in any order very quickly. It runs data simultaneously as compared to the other memories which store data inside the mind.
SRAM and DRAM are the two main types of RAM.
Table of Contents
SRAM and Dram
SRAM stands for Static Random Access Memory. It is an off-chip memory. It possesses our computers to store each bit. Until power is applied, the data will remain stored in static RAM.
DRAM stands for Dynamic Random Access Memory. A type of memory used by our computers for program codes and data, which helps the processor to function. It depends upon the applied voltage.
Now, after this basic definition, I am going to begin the actual differentiation below.
SRAM
SRAM is a semiconductive memory. Electronics, general computing applications, and microprocessors use it for memory purposes. It provides a direct interface with the CPU. The most useful point of SRAM is that data is static in it. Refreshing information is not required, which makes it faster. It is volatile memory because it can hold that until the power is on.
Let’s discuss the construction of static RAM.
Transistors are the building block of SRAM. It consists of six transistors, which is why it is called a 6T memory cell along with two cross-coupled resistors. Two of the conductors controls access to memory during the read and write process.
Sometimes more than six transistors are used. It can be 8T or 10T for introducing extra ports for static RAM. It has two bistable states, “0” and “1” because of a flip-flop, which performs latching in its circuit and holds each memory bit.
Now I will discuss the essential operation of SRAM.
The memory cells of SRAM arranged in a matrix. Its function is quite straightforward. When a battery gets selected, it stores the value, which is to write in flip-flops. The whole row of cells can be chosen together too to read contents by SRAM. Each cell is addressable.
Word line is the access to the SRAM memory. Two access transistors used in the structure of SRAM, and this process control these two transistors. It decides whether the cell should connect to the bit lines or not. These bit lines work as data transferring lines for reading and writing operations.
DRAM
Dynamic Random Access Memory stores data and codes which help the microprocessor and computer to perform the task. It can access any part of the memory directly. It works differently as compared to the SRAM.
In computers, it is more convenient to implement main memory as DRAM in comparison with SRAM. In DRAM, data needs to refreshed so that data can retain. The DRAM is not faster than SRAM but faster than some memory components.
Let’s make it easy for you guys by elaborating its structure first and then its functionality.
Only one capacitor and a single transistor can make DRAM. A capacitor is used to store every bit of data and a transistor (MOSFET) as a switch. DRAM has six times greater capacity than SRAM because of the use of a capacitor. There are two lines “word line” (rows) and “bit line” (column) connecting the circuit.
Now, why should you know how DRAM works?
So, it has also two states, “0” and “1”. O represents that there is no charge on the capacitor, while one shows that cost is present in a capacitor.
The whole structure lies on a silicon wafer where there the intersection of bit lines and word lines constitutes the addresses of a memory cell. DRAM works when the charge sent to the specific column by which transistor gets activate at each bit in the column.
While writing, the capacitor considers the state that row lines contain. But while reading, the charge is dependent upon the sense of amplifier if the charge level is higher than 50 percent, than it read as 1 and otherwise obviously 0.
A counter records the track record of rows accession. Seventy nanoseconds are an average time that is required to read and recharge each cell in a memory chip.
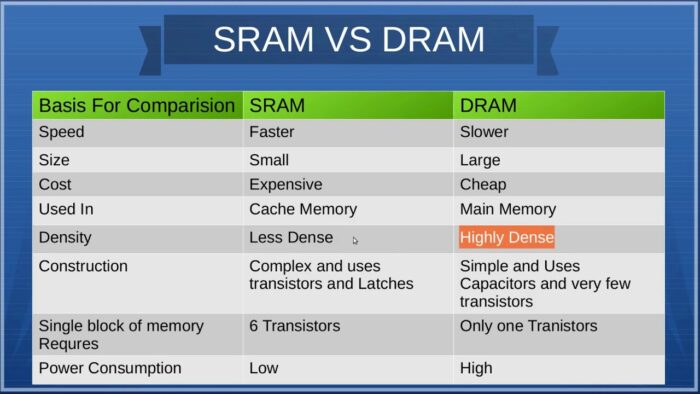
Difference Between SRAM and DRAM
I will illustrate the most important attributes of both SRAM and DRAM, which will make them differentiable.
I have explained to you SRAM and DRAM both in detail first. Now I will make a comparison. This comparison will make it easy for you to decide and which is more suitable for you.
TYPE
- The DRAM is an off-chip memory.
- SRAM is an on-chip memory.
POSITION
- The DRAM placed in the processor at the motherboard.
- SRAM lies between the main memory and the processor.
CAPACITY
- DRAM has large storage capacity.
- SRAM has less storage capacity.
COST
- The DRAM is not very expensive and cost-effective.
- SRAM is expensive but not cost-effective.
DENSITY
- The chip of DRAM is dense; it means DRAM is dense.
- SRAM is rarely dense.
VOLATILITY
- DRAM should be charged with standard charges and must have an active power supply. A constant power supply is not required.
- SRAM does not require any extra charges. As it is power dependent, that is why power off may cause data loss. It requires a constant power supply.
PERFORMANCE
- DRAM performs quite slowly. It takes a longer time to access.
- SRAM works at the speed of the microprocessor. It takes minimal time to access.
STRUCTURE
- The DRAM is made up of capacitors that store charges.
- SRAM is made up of flip flops.
SIZE
- The DRAM is large.
- SRAM is small in size.
USED IN
- The DRAM used in min memory.
- SRAM used in cache memory.
REFRESH
- Refreshing circuitry should require in DRAM.
- Refreshing circuitry should not require in SRAM.
DATA
- DRAM stores data in separate capacitors.
- SRAM stores data in latch until power is there.
These are the few points that cause a significant difference between SRAM and DRAM.
One of the most asked questions of readers is how much SRAM is faster than DRAM?
You will find the answer to this question in my article above, but I am explaining here briefly. SRAM has no refresh cycles. It consists of six transistors on the contrary. DRAM consists of one transistor along with the capacitor.
When I did not know about this topic, I used to get confused so many times. I used to ask people is DRAM more expensive than an SRAM?
The answer was always no, and still no. You can find the reason for this article.
FINAL WORDS
It becomes difficult when you have to differentiate two things, along with their excellent properties and bad points.
SRAM has to preferred over DRAM as SRAM consumes less power and faster than DRAM. But DRAM is less expensive, and now it has more storage areas.
Another reason to prefer SRAM is the refresh rate. SRAM does not need to refresh, but if we talk about DRAM, it needs to get updated in a few milliseconds to keep the charges.
I have tried to cover almost complete information about SRAM and DRAM and the difference between them. From structure to properties, I have described these memories accurately.
Now what you guys have to do is read my article first and, based on your analysis, choose between SRAM and DRAM. After reading and applying this article’s information, do not forget to share your feedback.